Content and Connection Control in Email Security
Content Filtering
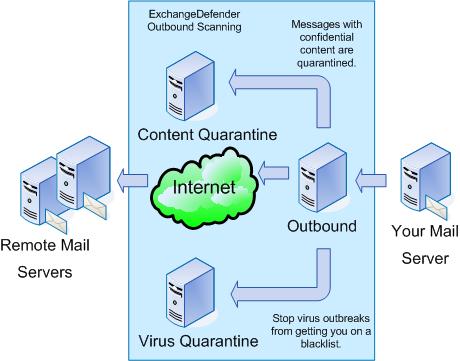
Both inbound and outbound mail can be scanned and filtered based on content. Each message will be decomposed, completely analysed including deeply embedded files.
Content filtering can be applied to policies depending on routes and contents specified. Scanning of SMTP header fields such as X-headers and received headers, content such as attachments and within the body are analysed and determined to take appropriate action.
Many file types such as audio, video, documents, and potentially dangerous files like exe and batch files can be blocked. Even if the extension of such files were changed, email filters are now clever enough to ignore these changes. They recognise files by their characteristics and do not have to rely on extensions anymore.
Content filtering occurs after connection based filtering.
Connection control
Connection control handles and controls the SMTP connections before emails are analysed by any content control features. Below is a list of connection control features.
Maximum concurrent connections - Maximum concurrent connections to the SMTP port that is accepted.
Maximum number of messages allowed per connection - Maximum emails from a single connection accepted.
Maximum number of received header - Maximum headers to the SMTP port the Proxy server accepts.
Maximum number of recipients - Maximum recipients for a single message that is accepted
Connection timeout - measured in seconds, that a single connection to the SMTP port remains open.
Listening port number - The port your server will listen on for SMTP email connections, which is almost always port 25.
Maximum message size - The maximum size of the email message usually measured in kilobytes or megabytes accepted.
Other connection control techniques are used as well, such as blocking emails via their IP address, domain name and individual email addresses.
Connection control features such as the above do not only block spam messages, but help reduce DOS and DDOS attacks, and also by dropping messages at the very first layer of a spam firewall, they will not have to scanned by any content filters. This helps the spam firewall continue performing effectively, as content filters do take up a lot of memory and processing power.